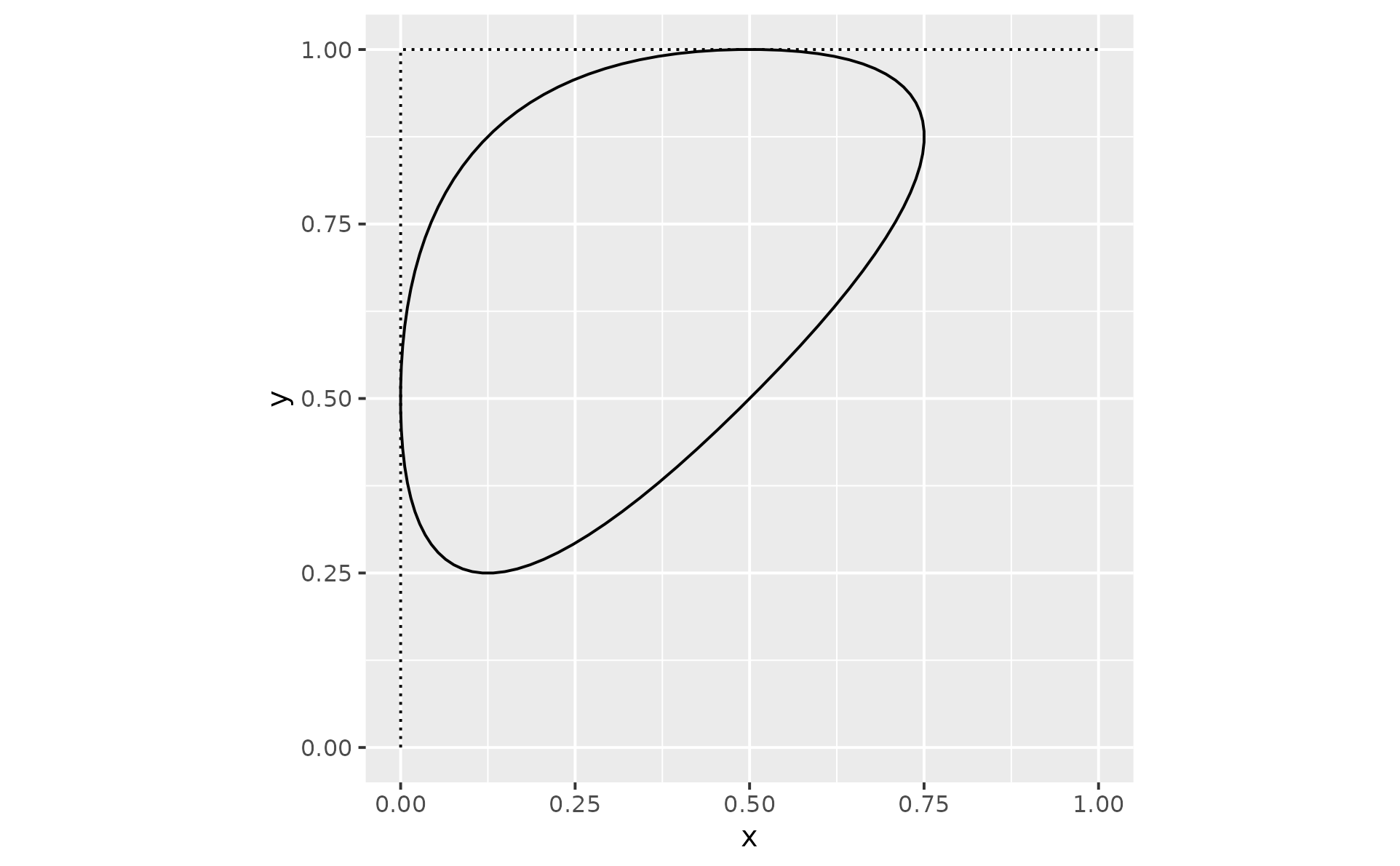
Apply Chaikin's corner cutting algorithm to smooth a path
Source:R/geom-chaikin.R, R/stat-chaikin.R
geom_chaikin.RdChaikin's corner-cutting algorithm can be used to smooth sharp corners of a path.
Usage
geom_chaikin(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "chaikin",
position = "identity",
...,
mode = "open",
iterations = 5,
ratio = 0.25,
arrow = NULL,
arrow.fill = NULL,
lineend = "butt",
linejoin = "round",
linemitre = 10,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
stat_chaikin(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = "path",
position = "identity",
...,
mode = "open",
iterations = 5,
ratio = 0.25,
closed = lifecycle::deprecated(),
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes(). If specified andinherit.aes = TRUE(the default), it is combined with the default mapping at the top level of the plot. You must supplymappingif there is no plot mapping.- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options:
If
NULL, the default, the data is inherited from the plot data as specified in the call toggplot().A
data.frame, or other object, will override the plot data. All objects will be fortified to produce a data frame. Seefortify()for which variables will be created.A
functionwill be called with a single argument, the plot data. The return value must be adata.frame, and will be used as the layer data. Afunctioncan be created from aformula(e.g.~ head(.x, 10)).- position
A position adjustment to use on the data for this layer. This can be used in various ways, including to prevent overplotting and improving the display. The
positionargument accepts the following:The result of calling a position function, such as
position_jitter(). This method allows for passing extra arguments to the position.A string naming the position adjustment. To give the position as a string, strip the function name of the
position_prefix. For example, to useposition_jitter(), give the position as"jitter".For more information and other ways to specify the position, see the layer position documentation.
- ...
Other arguments passed on to
layer()'sparamsargument. These arguments broadly fall into one of 4 categories below. Notably, further arguments to thepositionargument, or aesthetics that are required can not be passed through.... Unknown arguments that are not part of the 4 categories below are ignored.Static aesthetics that are not mapped to a scale, but are at a fixed value and apply to the layer as a whole. For example,
colour = "red"orlinewidth = 3. The geom's documentation has an Aesthetics section that lists the available options. The 'required' aesthetics cannot be passed on to theparams. Please note that while passing unmapped aesthetics as vectors is technically possible, the order and required length is not guaranteed to be parallel to the input data.When constructing a layer using a
stat_*()function, the...argument can be used to pass on parameters to thegeompart of the layer. An example of this isstat_density(geom = "area", outline.type = "both"). The geom's documentation lists which parameters it can accept.Inversely, when constructing a layer using a
geom_*()function, the...argument can be used to pass on parameters to thestatpart of the layer. An example of this isgeom_area(stat = "density", adjust = 0.5). The stat's documentation lists which parameters it can accept.The
key_glyphargument oflayer()may also be passed on through.... This can be one of the functions described as key glyphs, to change the display of the layer in the legend.
- mode
Character. Should the geom draw a closed polygon or an open path? Must be one of
"open"(default) or"closed".- iterations
Integer. Number of iterations to apply between
1and10. Wheniterations = 0the original data is unchanged so essentially this is the same as callingggplot2::geom_path(); however this might be useful when you want to toggle smoothing on/off programmatically without removing the layer.- ratio
Numeric. Cutting ratio must be a number between
0and1. Ifratio > 0.5, then it will be flipped to1 - ratio.- arrow
Arrow specification, as created by
grid::arrow().- arrow.fill
fill colour to use for the arrow head (if closed).
NULLmeans usecolouraesthetic.- lineend
Line end style (round, butt, square).
- linejoin
Line join style (round, mitre, bevel).
- linemitre
Line mitre limit (number greater than 1).
- na.rm
If
FALSE, the default, missing values are removed with a warning. IfTRUE, missing values are silently removed.- show.legend
logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
NA, the default, includes if any aesthetics are mapped.FALSEnever includes, andTRUEalways includes. It can also be a named logical vector to finely select the aesthetics to display. To include legend keys for all levels, even when no data exists, useTRUE. IfNA, all levels are shown in legend, but unobserved levels are omitted.- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics, rather than combining with them. This is most useful for helper functions that define both data and aesthetics and shouldn't inherit behaviour from the default plot specification, e.g.annotation_borders().- geom, stat
Use to override the default connection between
geom_chaikin()andstat_chaikin().- closed
Value
A ggplot2::layer() object that can be added to a ggplot2::ggplot().
Details
Chaikin's corner cutting algorithm iteratively turns a jagged path into a smooth path.
The recursion formula starts from two vertices A and B, which represent a single corner of your path. From this, the algorithm derives two new points: one at the specified ratio when going from point A to point B, and one when going from B to A in the opposite direction. By default, a ratio of 0.25 results in two points: the first at 25% of point A and the other at 75% of point A (or 25% of point B). Those new points form a smoother path. Then the algorithm applies the same rule to each pair of new points. The rule is applied iterations times. The maximum number of iterations is 10, default is 5.
References
Chaikin, G. An algorithm for high speed curve generation. Computer Graphics and Image Processing 3 (1974), 346–349
See also
The smoothr package offers tools to smooth and tidy spatial features
Aesthetics
geom_chaikin() understands the following aesthetics. Required aesthetics are displayed in bold and defaults are displayed for optional aesthetics:
| • | x | |
| • | y | |
| • | alpha | → NA |
| • | colour | → via theme() |
| • | group | → inferred |
| • | linetype | → via theme() |
| • | linewidth | → via theme() |
Learn more about setting these aesthetics in vignette("ggplot2-specs").
Examples
set.seed(42)
dat <- data.frame(
x = seq.int(10),
y = sample(15:30, 10)
)
p1 <- ggplot(dat, aes(x, y)) +
geom_line(linetype = "12")
p1 +
geom_chaikin()
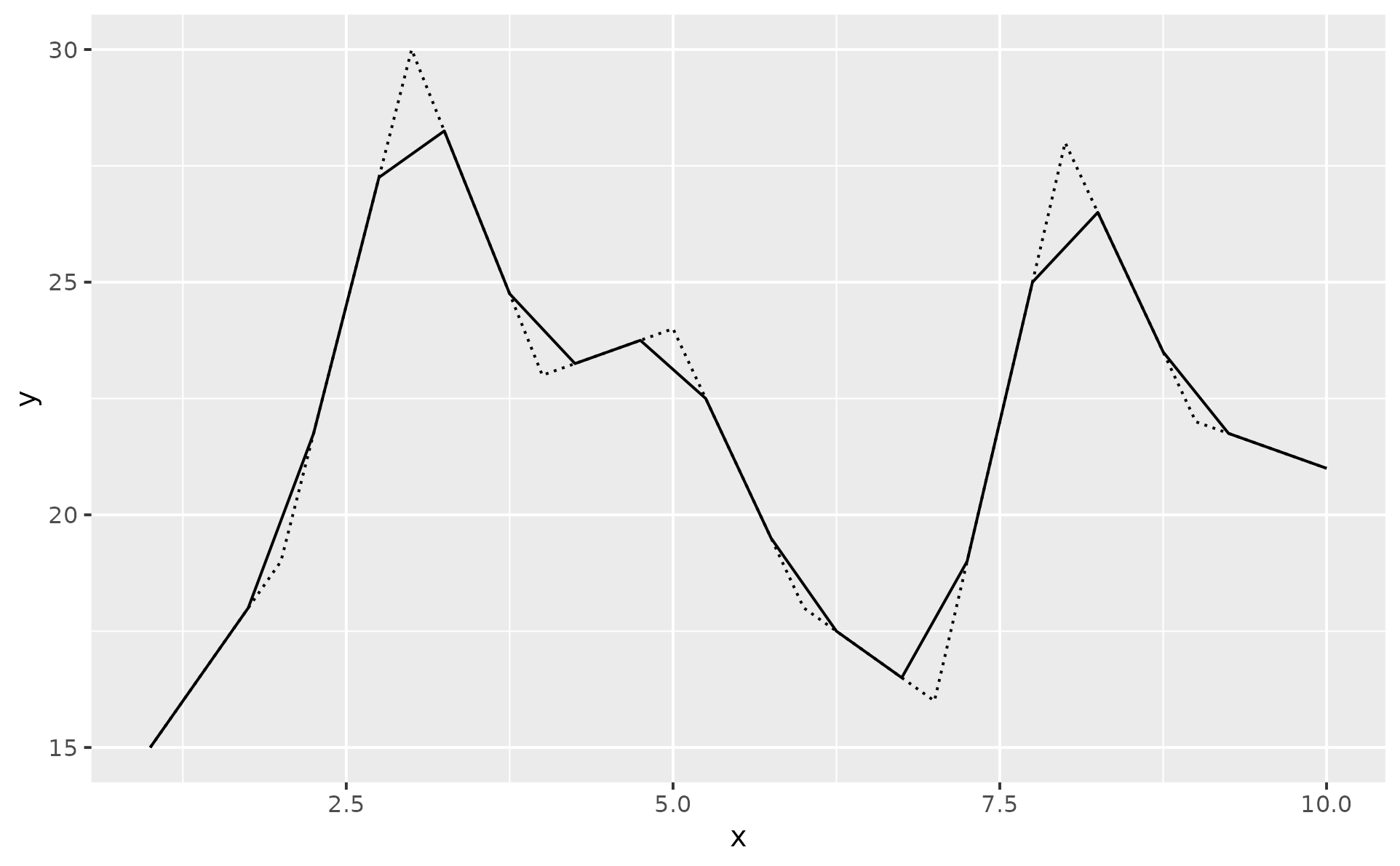
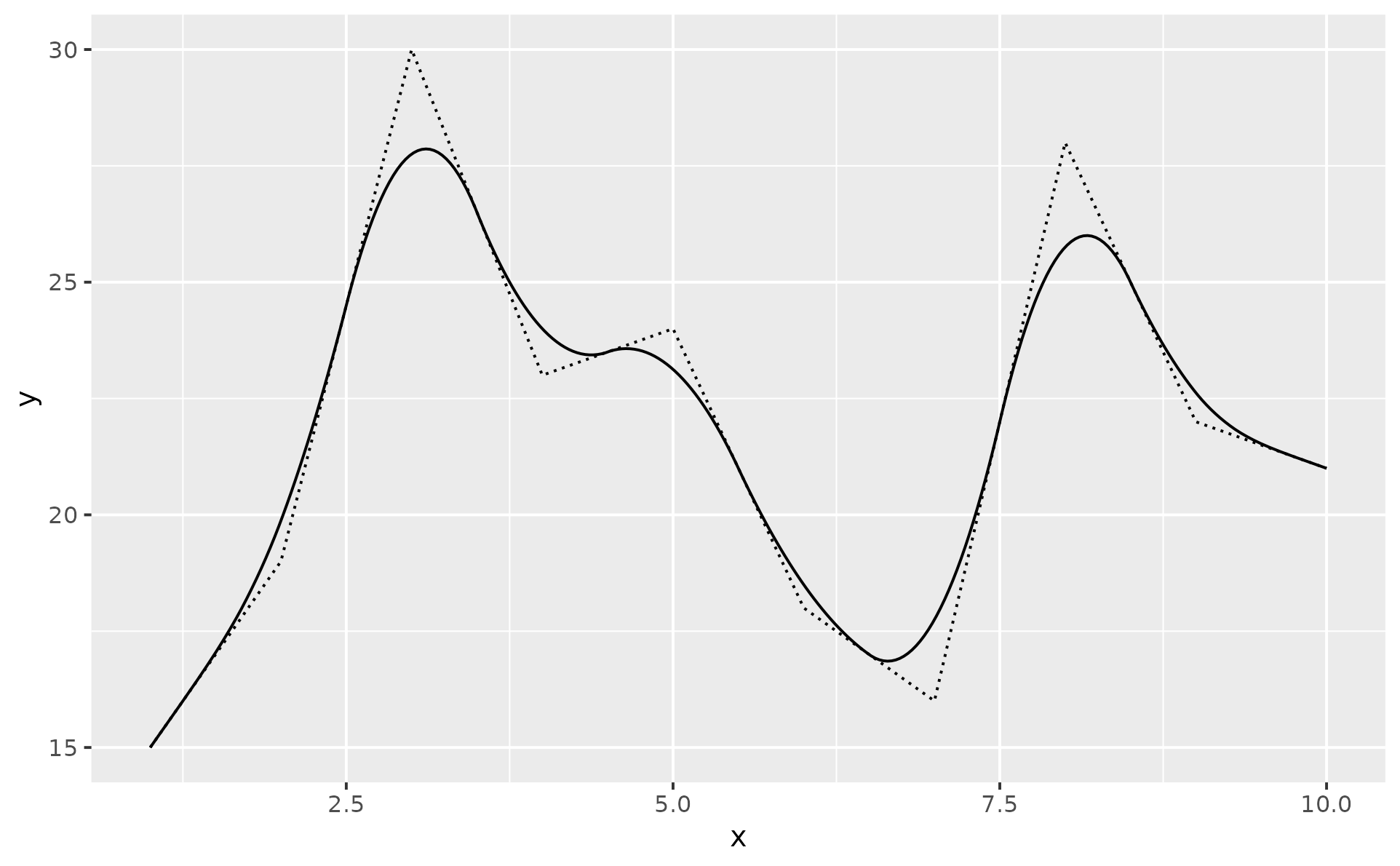 p1 +
geom_chaikin(iterations = 1)
p1 +
geom_chaikin(iterations = 1)
 triangle <- data.frame(x = c(0, 0, 1), y = c(0, 1, 1))
p2 <- ggplot(triangle, aes(x, y)) +
geom_path(linetype = "12") +
coord_equal()
# ratio lets you control the cutting amount
p2 + geom_chaikin(ratio = .1)
triangle <- data.frame(x = c(0, 0, 1), y = c(0, 1, 1))
p2 <- ggplot(triangle, aes(x, y)) +
geom_path(linetype = "12") +
coord_equal()
# ratio lets you control the cutting amount
p2 + geom_chaikin(ratio = .1)
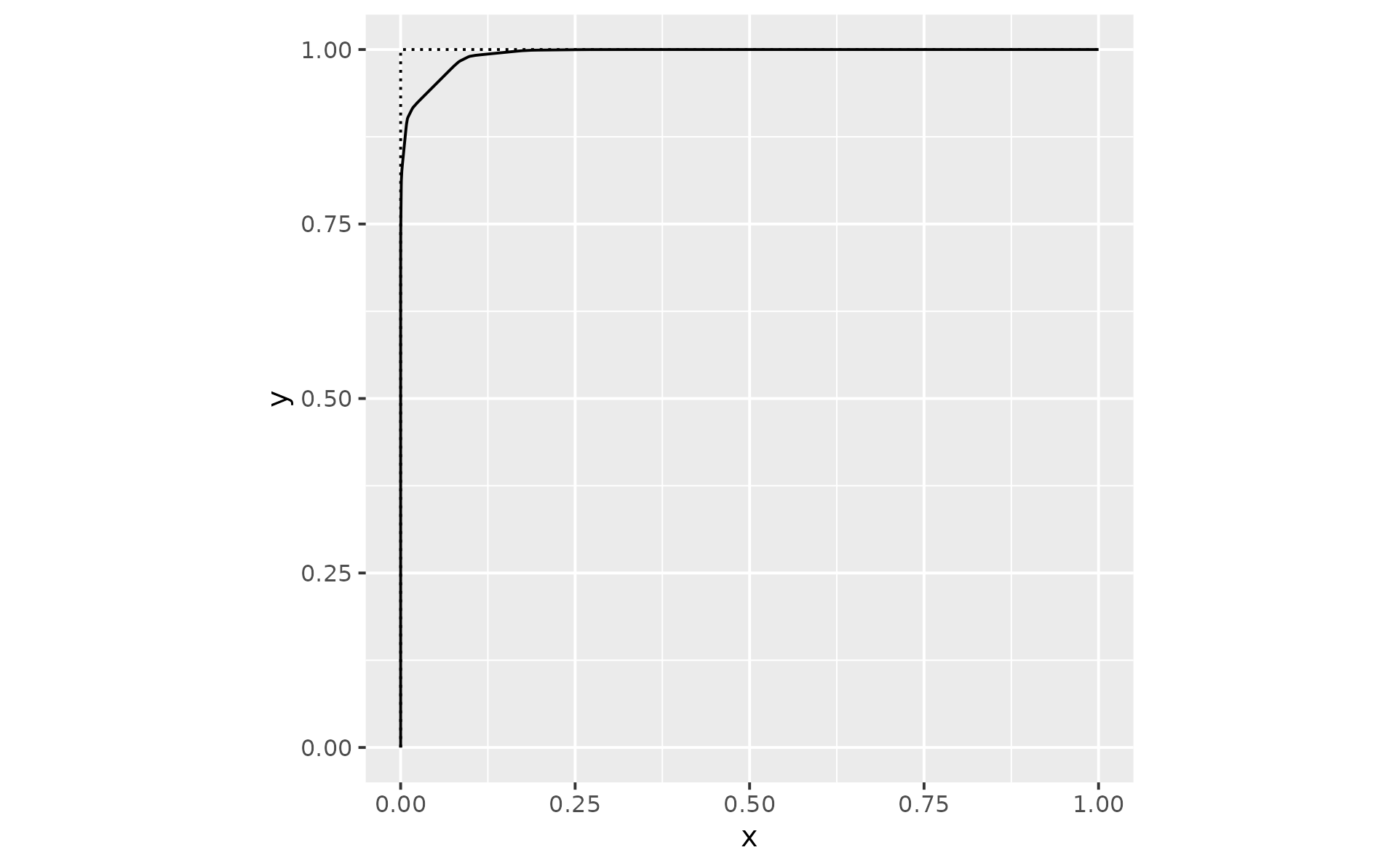 p2 + geom_chaikin(ratio = .5)
p2 + geom_chaikin(ratio = .5)
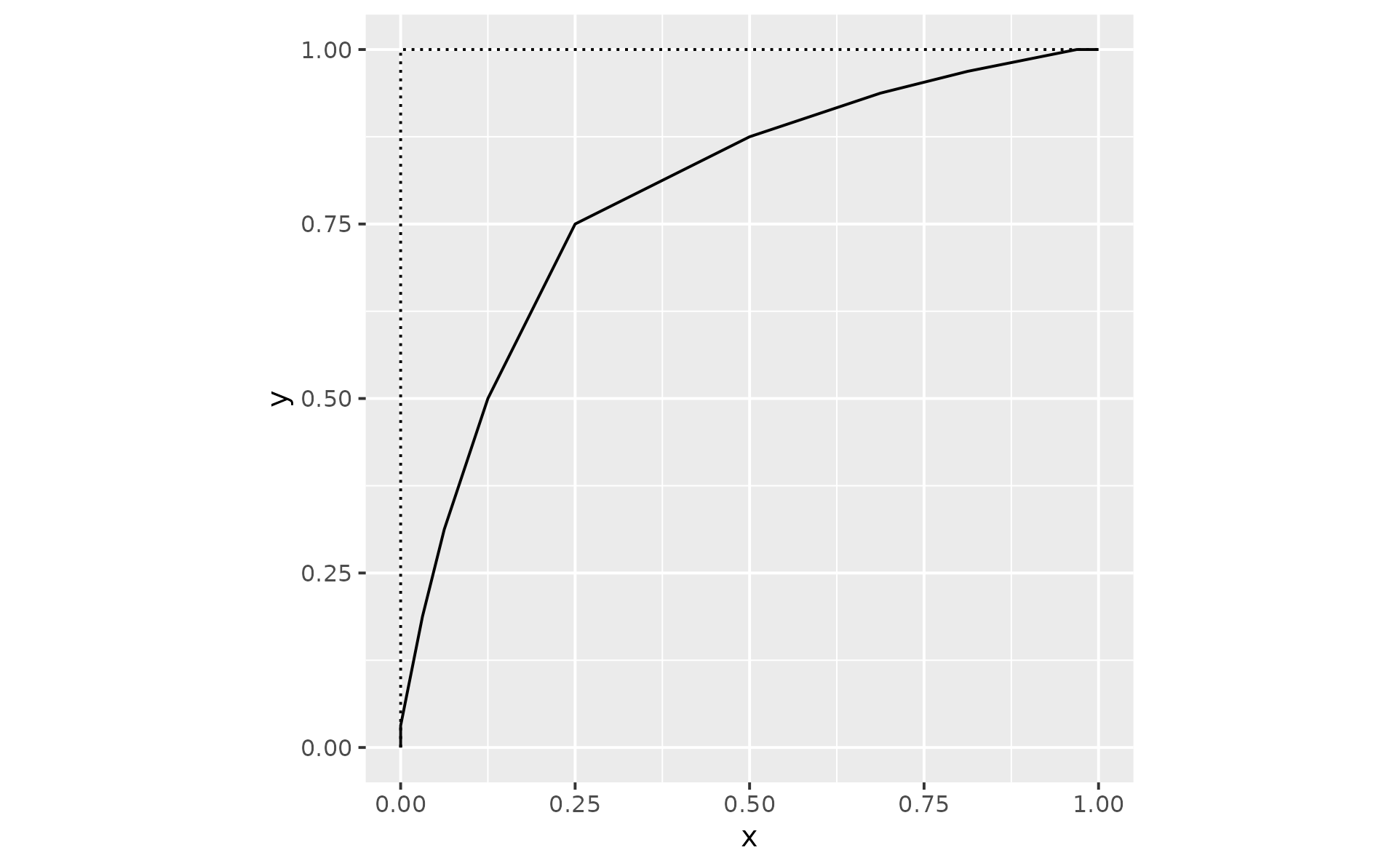 # mode controls whether the result is an open or closed shape
p2 + geom_chaikin(mode = "open") # default
# mode controls whether the result is an open or closed shape
p2 + geom_chaikin(mode = "open") # default
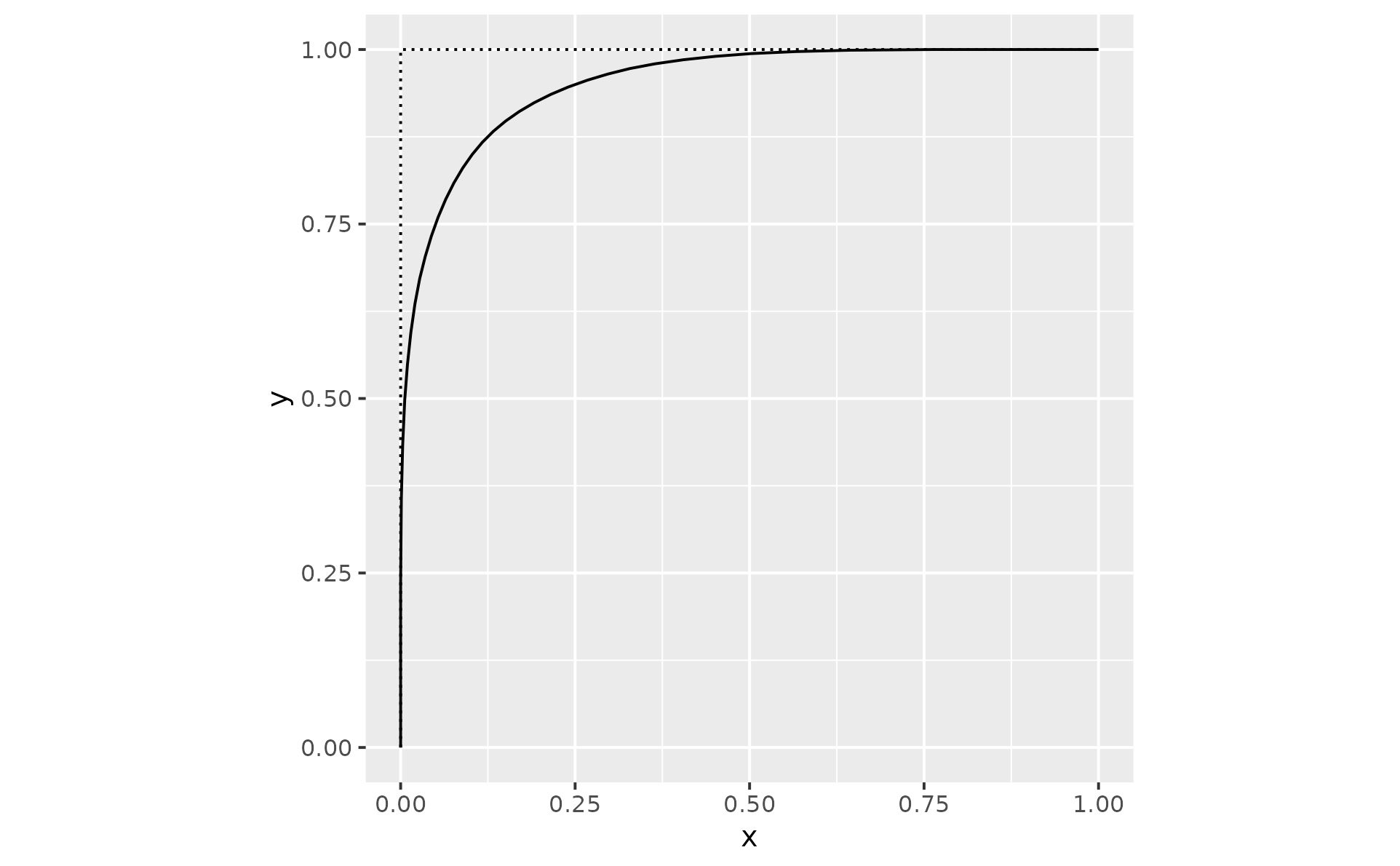 p2 + geom_chaikin(mode = "closed")
p2 + geom_chaikin(mode = "closed")